目的
对于目前DNNs网络越来越大,越来越深,而GPU的内存有限训练大型的DNN网络面临困难(显存不够用)。
方法
在训练DNNs时占用显存的数据结构分为四部分:feature maps, weights, gradients, 和 workspace.
- Feature maps are the intermediate results that are consumed in the following forward or backward layers.
- Gradient maps are the intermediate results that are generated in the backward pass and consumed by the dependent layers.
- Weight value decides how much influence the input will have on the output.
- The workspace is the intra-layer storage to speed up the layer computation
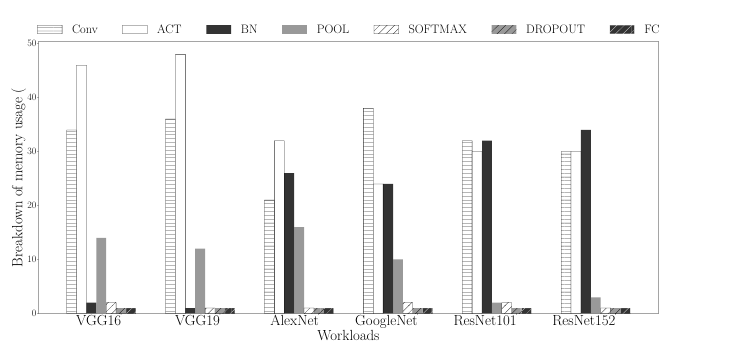
其中feature maps占用了大部分,比如Inception V4网络中feature maps占用了90%的显存。对于网路结构中不同的层显存占用也不一样,其中CONV,ACT,BN,POOL层占用了大部分。
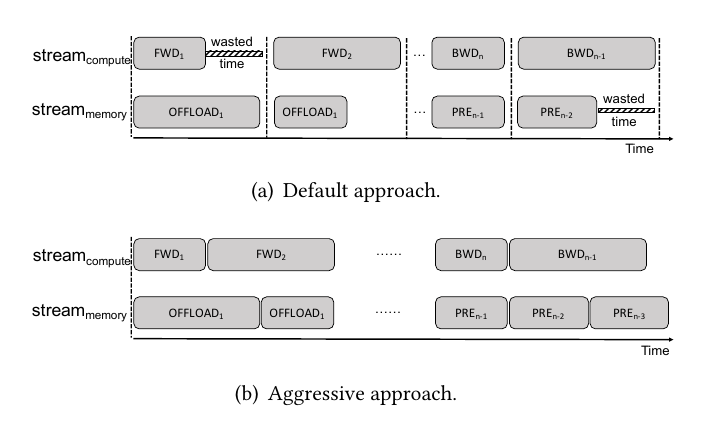
对于linear DNNs网络比如AlexNet, VGG,网络层是线性堆叠的,我们可以将暂时用不上feature map从显存转到CPU的内存去保存,而在需要的时候在调进显存,通过让通信时间与计算时间重叠来提高性能表现。
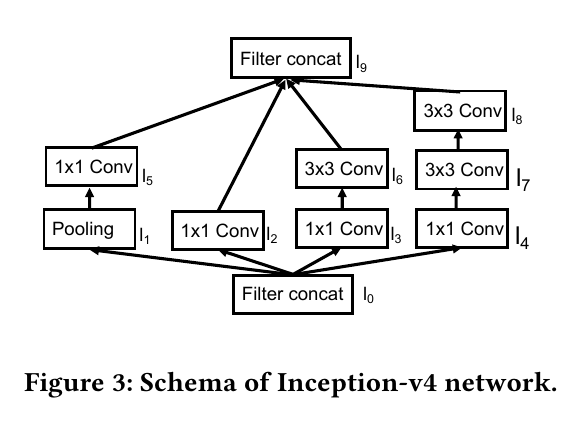
对于Nonlinear DNNs网络,它们的网络层之间的关系比较复杂,在判断某个feature maps是否可以转存到CPU内存比linear DNN网络会更复杂。本文通过对网络结构图进行DNS搜索来确定不同层的执行顺序,并来判定是否可以进行转存。
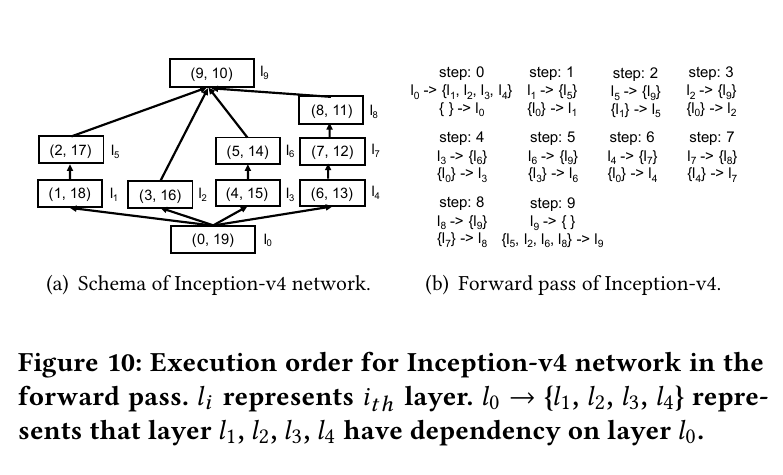
本文还发现这种大量的转存,分配空间会造成内存碎片的问题。
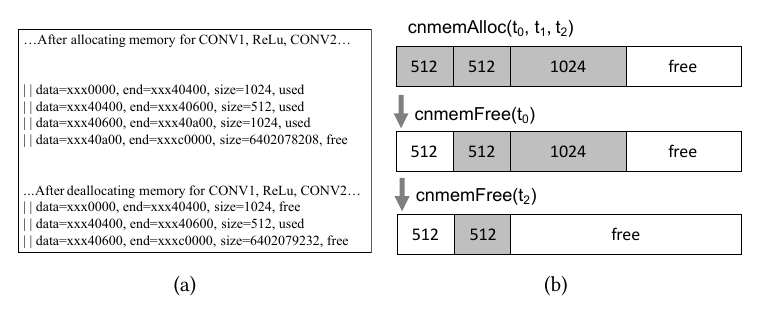 为了解决该问题作者主要的思想是 provide a soft guarantee that all of the tensors having the same dependencies or similar lifetime should be allocated in the same region.
为了解决该问题作者主要的思想是 provide a soft guarantee that all of the tensors having the same dependencies or similar lifetime should be allocated in the same region.